 Photo taken from https://arxiv.org/abs/2207.07305
Photo taken from https://arxiv.org/abs/2207.07305This project is a part of an term paper project in my 5th semester course IN232 (Introduction to Solid State Physics) instructed by Prof. Chandni Usha and Prof. Tapajyoti Das Gupta at IISc Bangalore. The project mostly concerned itself with the theoretical framework of k.p perturbation theory, along with its advantages and applications od calculating the band structures in Wurtzite type of materials. A small abstract is presented below:
“The k·p perturbation theory is a powerful method used in solid-state physics to calculate the electronic band structure of semiconductors and other crystalline materials. It is based on perturbing the wave functions near high-symmetry points in the Brillouin zone, particularly around the band edges, using a momentum operator (k·p). This approach simplifies the complex calculations required for determining energy bands, particularly near the conduction and valence band edges, by focusing on a few basis states rather than the entire band structure.
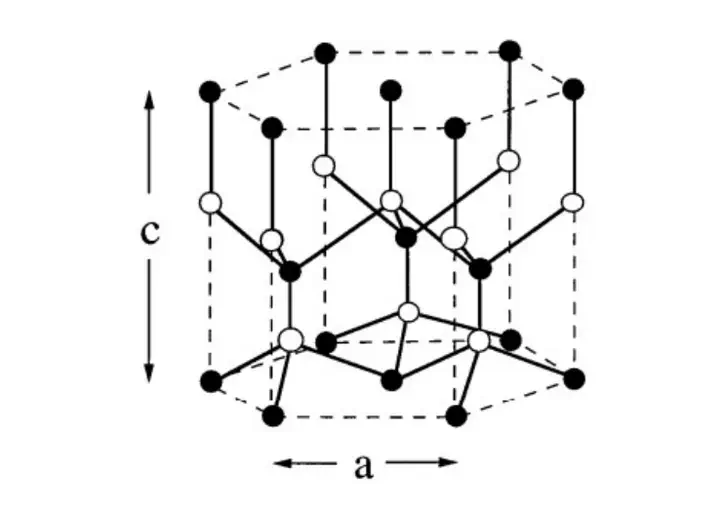
In wurtzite structures, such as those found in materials like GaN and ZnO, k·p perturbation theory is particularly useful. Wurtzite semiconductors have unique hexagonal crystal structures and exhibit strong piezoelectric effects, making their band structures more complex. Using k·p perturbation theory, researchers can accurately model and predict the electronic band diagrams, including bandgap energies, effective masses, and the impact of strain, which is critical for designing optoelectronic devices like LEDs and laser diodes.”