 Photo taken from https://arxiv.org/abs/2207.07305
Photo taken from https://arxiv.org/abs/2207.07305This project is a part of an insemester reading project under Prof. Baladitya Suri and his postdoc Athreya Shankar at IISc Bangalore. The project mostly concerned itself with the theoretical framework of non-linear oscillator in the form of van der pol oscillator. The theoretical part of the project pertains to understandimg the Quantum vdp ocillator and entropy production rates utilizing classical markov techniques, to see if there is a possibility of a quantum phase transition, which was not observed. A small abstract is presented below:
“Quantum Van der Pol oscillators are nonlinear oscillators that exhibit self-sustained oscillations even at the quantum level, driven by the balance between gain and loss mechanisms. These oscillators are significant in studying quantum synchronization, where quantum systems align their phases despite the inherent quantum noise. One of the notable applications of quantum Van der Pol oscillators is in phonon lasers, where they enable the generation and amplification of coherent phonons (quantized sound waves), similar to how traditional lasers amplify light. This is crucial for developing advanced phononic devices for precision measurements. Additionally, quantum Van der Pol oscillators have been proposed for ultra-sensitive force sensing. Due to their high sensitivity to external perturbations, they can detect minute forces at the quantum scale, making them invaluable in experiments requiring extreme precision, such as probing weak gravitational forces or measuring tiny mechanical displacements in quantum metrology.”
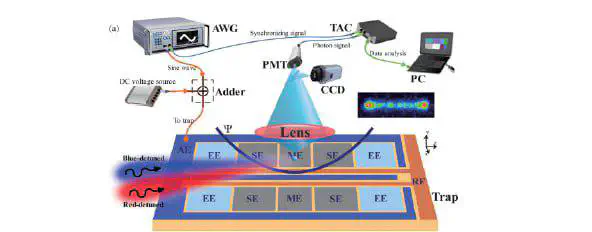
In the practical part, I summarise the utilization of Quantum VdP oscillators in Phonon lasers, for ultrasensitive sensing in ion traps, which is highlighted in the second part of the project report.